Let’s face it. The foundation of anything (house, structure, or marketing campaign) is the single most important piece of the overall plan. Build on a weak foundation, and you can expect a collapse.
The same goes for SEO.
Even the best off-page strategy won’t do much if the foundational on-page strategy is not properly in place. Every internet marketer knows and understands this, but I constantly see shoddy on-page optimization when reviewing websites.
After recently reviewing two websites with awful on-page SEO work, I was driven to write a detailed guide for new or experienced SEOs who want to effectively optimize their site on-page – the right way. To make this article as short and concise as possible, I have provided links to other great articles in order to expand on ideas that I believe require more in-depth reading, such as Schema markup and keyword research.

AUTHOR NOTE: Every SEO practitioner approaches on-page a little differently, especially in terms of where they start. This approach is my personal preference and is not listed in order of importance.
Website Page Errors

Your first step should be to review the site for broken links (404′s) or any temporary redirects (302′s). You can use a bunch of tools for this like Screaming Frog or Link Slueth.
Make a list of all the links that need to redirected and do so either via HTACCESS or via your favorite CMS plugin or control panel.
For 404 errors, you want to make sure the broken page is redirected to the appropriate new page. If none exist on your new site, redirect it to the homepage, so you keep all your link equity.
For any 302 pages, make sure they are converted to 301 eventually. This step should ensure your site is easier to crawl for both visitors and search engine bots.
Website URL Canonicalization
For this step, I would use one of the website analysis tools mentioned above to make sure none of the pages have duplicate URLs. Make sure the non-www 301 redirects to the www version or vica versa.
Another important aspect often overlooked are URL extensions that sometimes show up as duplicates. For example, you find that there are two URLs like www.site.com and www.site.com/home.php or www.site.com/home.asp.
Make sure there is only one version for all URLs. Anymore and you’re going to be penalized for duplicate content. You can easily check this by running Screaming Frog and sorting all the URLs by name, and you will quickly see any closely named URLs. Once you find all the duplicate URL’s, make sure you 301 them to the appropriate page. Also, make sure if you have an e-commerce website, all the canonical pages have a “rel-canonical” tag in place.
Every time a page is sorted for price or rating, it creates a whole new page/URL, which needs the relevant re-canonical tag inserted on it. Here is a great article on rel-canonical tags from Google.
Keyword Research
There are many great resources that can be found on this topic, so there’s no need for me to re-hash old information. Make sure you read a few articles and do proper keyword research for all the relevant pages.
This is the single most important step in a successful SEO campaign.
This recent SEJ article on keyword research is worth reading for additional insight.
Metadata Implementation (Title, Meta Description, H1 & ALT)
After you have done proper keyword research, the next logical step is to create compelling metadata tags for all your relevant pages.
Title Tags
Personally, I have steered away from the old days of creating title tags like: Keyword 1 | Keyword 1 | Brand Name
I prefer writing more descriptive title tags that read like a sentence (think Hummingbird update). Something like:
Internet Marketing News & Tips | SEJ
A descriptive title tag reads more naturally and it’s probably better for conversions as well. Also, make sure the title tags are within the new recommend length of 55-60 characters. Anything more and you will see your title tags truncated in search results, which kills user experience.
Meta Description
These are not calculated in search engine rankings, but they are read by searchers to better understand what a page is about. It can also be effectively used as a call to action for your product or service.
Make sure you use your meta description to entice searchers to click on your website over all others. The recommended character limit for meta description tags is between 155-160 characters.
H1
Depending on the page, try to incorporate a descriptive H1 tag with relevant keywords without going overboard. Your goal is to give your audience the best user experience.
ALT Tags
While you’re optimizing all the tags, you should also optimize the images. Try and incorporate descriptive ALT tags for all images. Who know? They could show up in a Google image search and bring in some relevant traffic via that channel.
Site Load Speed

Use the Google Page Insight tool to see how fast your website loads. It has long been known that Google incorporates site speed into its search rankings. And this is for good reason. As a user, I personally hate slow loading websites. Google has taken note of this and gives preference to faster loading websites.
Depending on the size of your site, a good average is at least 90+ for both desktop and mobile versions. If your site falls short, take Google’s recommendation and hand them to the site Webmaster for implementation. Sometimes, it could be as easy as tweaking the HTACCESS file, but sometimes it could mean changing the image size or JavaScript.
XML Sitemap
Make sure the site has an XML sitemap created. The easiest way to check for this is to type in www.site.com/sitemap.xml.
If you see a 404 page or the homepage show up, this means there is no XML sitemap. This type of sitemap is recommended by all the major search engines (Yahoo and Bing, too) and helps search bots know how many pages your site has.
There are several tools that will create an XML sitemap for you. Create one and place it in the root directory of your website via FTP or you can use your favorite plugin for WordPress or any other CMS system you are using,
Social Media Icons

Make sure you have signed up for the major social media accounts such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Google+. Then, take it one step further and insert those social media icons on your website. This helps Google bots make a direct connection with your website’s social media pages, but it also helps user experience as it provides an extra layer of credibility when searchers land on your website.
Let’s face it, what company does not have social media profiles these days? When I see a site without one, it raises suspicions about their credibility.
Content/Copy Optimization
There are several studies around long versus short copy. Without getting into it, my personal recommendation would be to go for at least 500+ words of relevant copy for each of the important pages.
Obviously the “Contact Us” page will not have a lot of content (generally speaking). Additionally, having more content cannot hurt your site, but less content can make your website come across as “thin”.
Hire a good copywriter to create some relevant and compelling content. It will help both conversion and search engine visibility.
Schema Markup
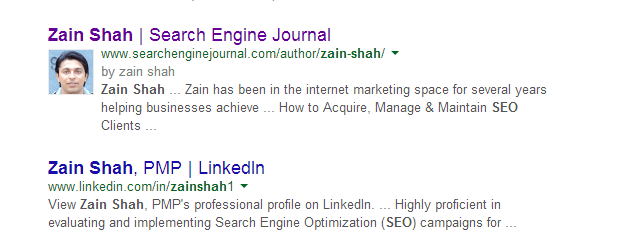
Screenshot Taken June 2014
For those unfamiliar with this markup, it helps search engines better understand specific information about your site, like the official business name and address, and displays this information correctly on result pages.
If you have products for sale, it helps Google list reviews and ratings right on the SERPs. If you’re an author, it would display your author picture next to your articles. This greatly increases the click-through rate (CTR) as searchers can see exactly how popular a product is without even clicking on a result.
It is essential that your site has some form of Schema markup implemented. You can read this great guide from SEJ on how to implement schema for various websites.
Website Structure and Architecture (aka Internal Linking)
Always ensure that all your pages are connected in a hierarchy via the main navigation. This can also be referred to as a “silo structure”.
Essentially, this means there is a logical order of all your products and services. For example, a page about cars should further break down into types of cars. The URL structure should look something like this:
- www.site.com/cars/sedans
- www.site.com/cars/convertibles
- www.site.com/cars/coupe and so on.
This helps searchers (and search engine bots) make logical connections between all the different pages on your website.
Also make sure that all the pages on your site are interconnected to avoid creating “orphan” pages or a page that is not connected via a navigation or any other page. Google bots find pages by following links, and a page that isn’t linked internally won’t be indexed on search engine.
Here is a great SEJ article that goes into detail on how to properly implement site architecture